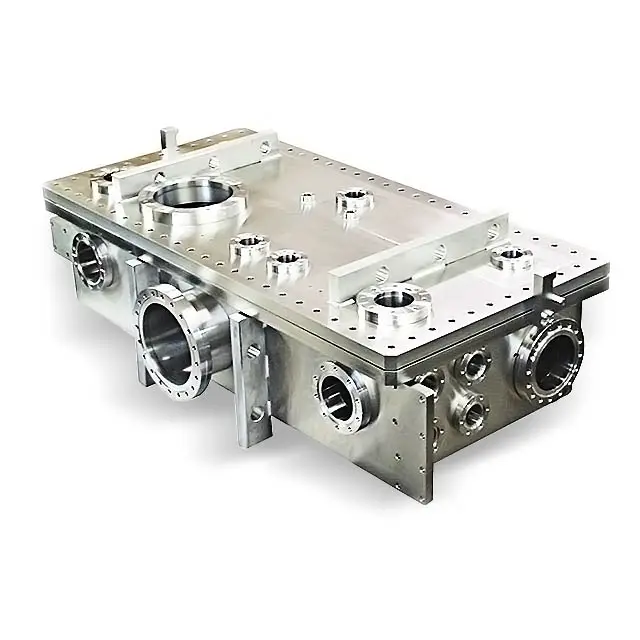
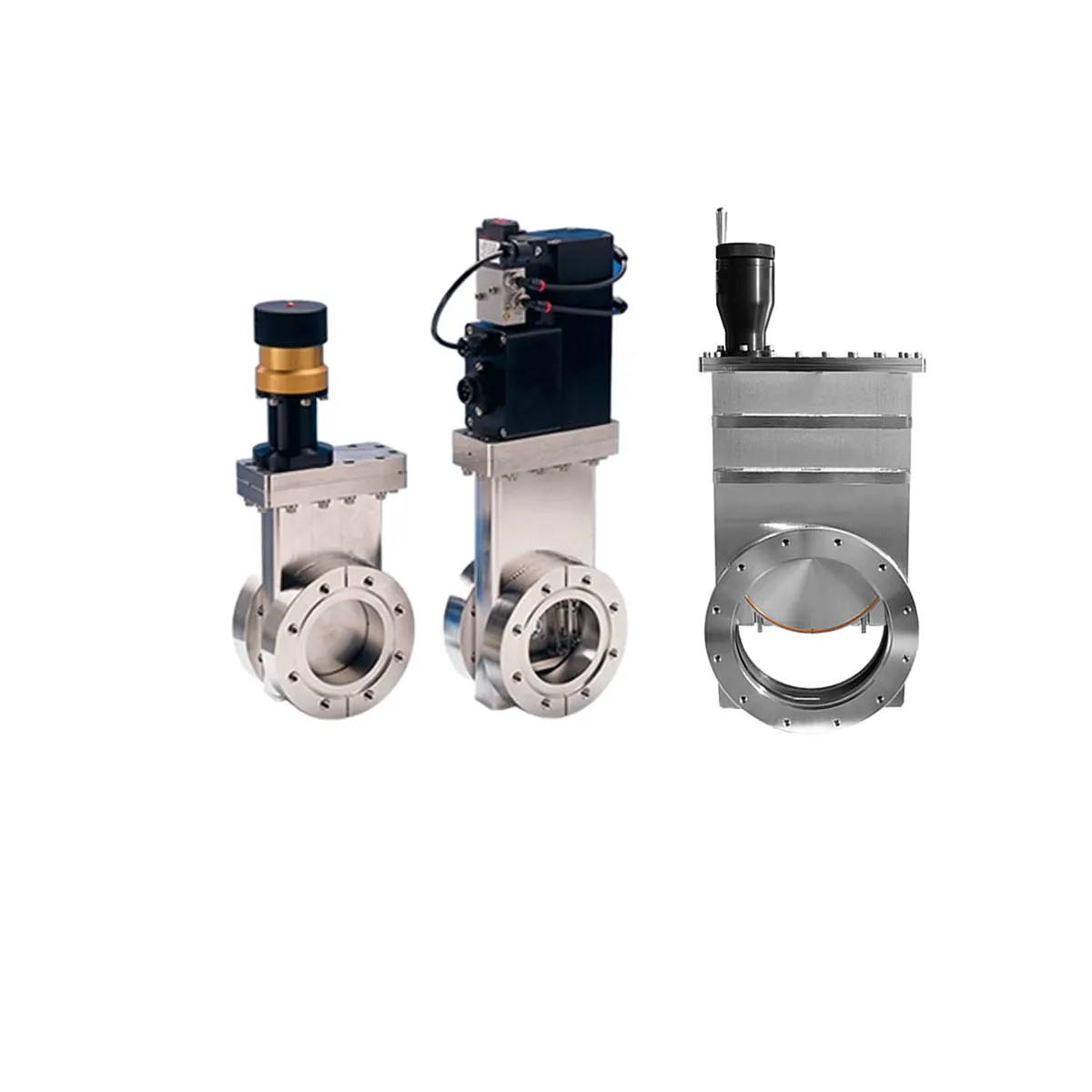
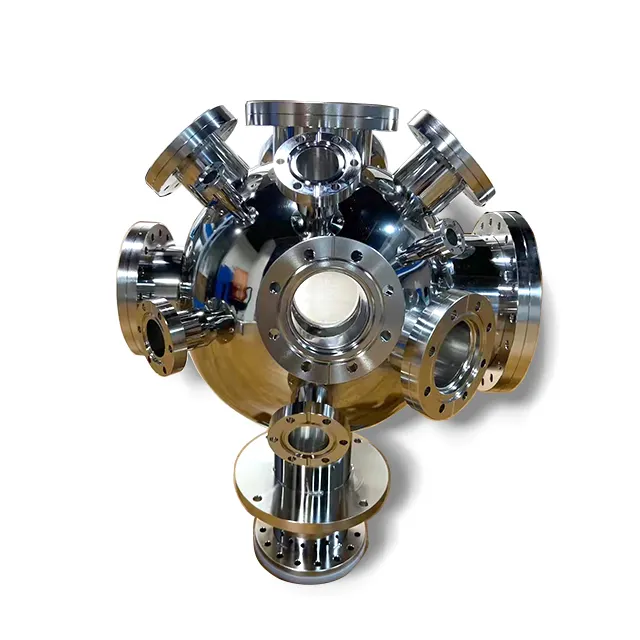
parts of a vacuum pump
A vacuum pump consists of several essential parts working together to create and maintain vacuum conditions. The main components include the inlet and outlet ports, which control the flow of air and gases. The pump chamber houses the working mechanism, typically featuring rotors, vanes, or pistons depending on the pump type. The drive system, consisting of an electric motor and transmission components, provides the necessary mechanical power. Seals and gaskets are crucial for maintaining vacuum integrity, preventing leaks that could compromise performance. The cooling system, including fans or liquid cooling mechanisms, regulates operating temperature to ensure optimal efficiency. Oil-lubricated pumps include an oil reservoir and distribution system, while dry pumps employ special materials and coatings for friction reduction. Control systems and sensors monitor and adjust pump operation, offering features like pressure regulation and safety shutoffs. These components work in concert to achieve various vacuum levels, from rough vacuum for basic industrial processes to high vacuum for specialized applications in semiconductor manufacturing, scientific research, and medical equipment. The durability and reliability of these parts determine the pump's overall performance and longevity.